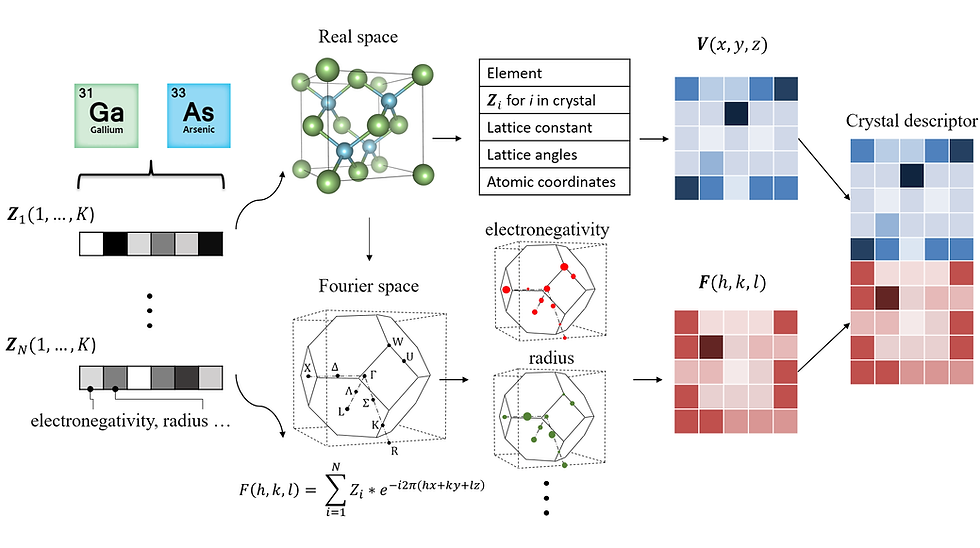
Deep learning has fostered many novel applications in materials informatics. However, the inverse design of inorganic crystals, i.e. generating new crystal structure with targeted properties, remains a grand challenge. An important ingredient for such generative models is an invertible representation that accesses the full periodic table. This is challenging due to limited data availability and the complexity of 3D periodic crystal structures. In this paper, we present a generalized invertible representation that encodes the crystallographic information into the descriptors in both real space and reciprocal space. Combining with a generative variational autoencoder (VAE), a wide range of crystallographic structures and chemistries with desired properties can be inversedesigned. We show that our VAE model predicts novel crystal structures that do not exist in the training and test database (Materials Project) with targeted formation energies and band gaps. We validate those predicted crystals by first-principles calculations. Finally, to design solids with practical applications, we address the sparse label problem by building a semi-supervised VAE and demonstrate its successful prediction of unique