December 2021: Scientific Reports
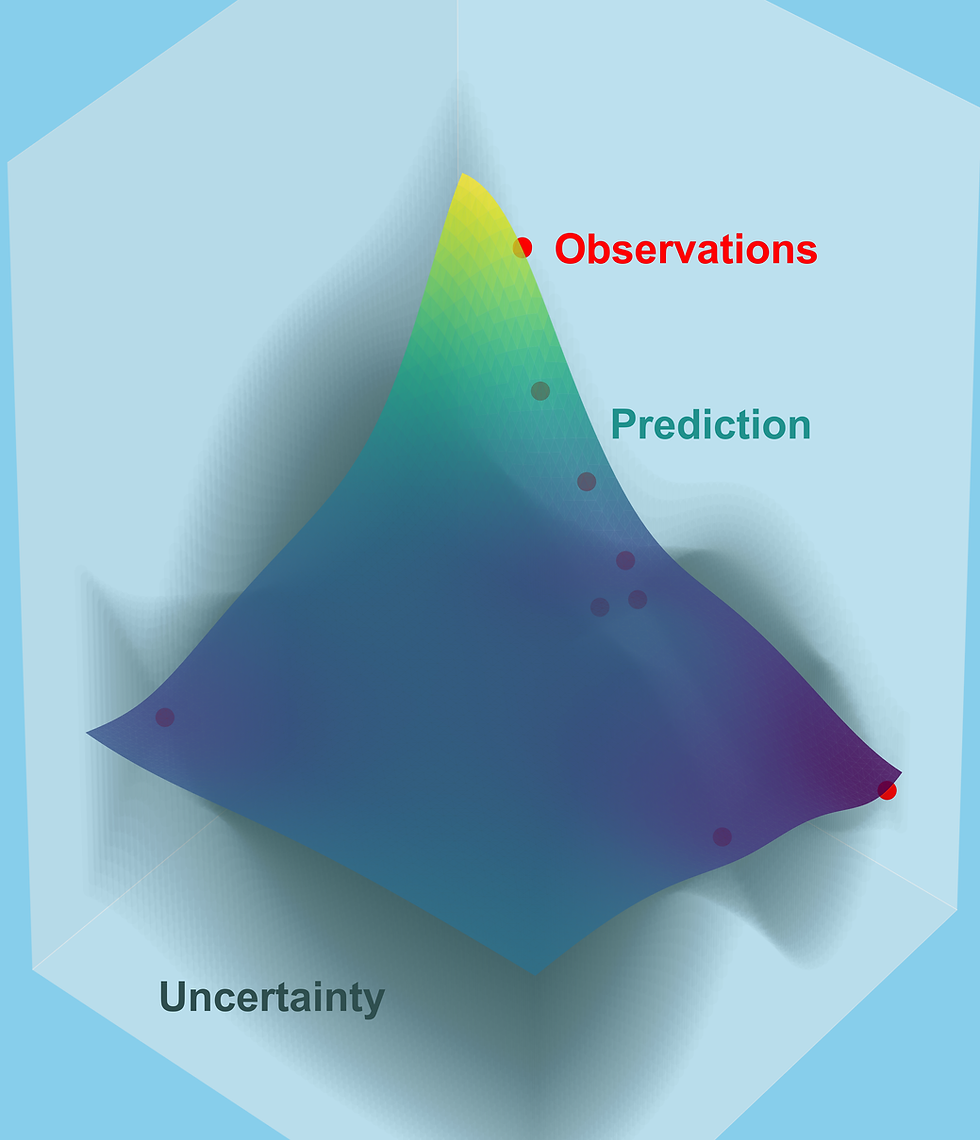
Despite the surfeit in the amount of research interest towards organic semiconductors in the last few decades, the underlying charge transport picture still remains hazy with no consensus among the different models. Here, we employ a purely data-driven approach, namely symbolic regression, on temperature-dependent field-effect mobility data of different organic semiconductors to describe the transport and compare the same with a physics-inspired renormalization fitting approach where we used a scaled, dimensionless mobility with respect to a scale-invariant reference temperature. We find that the renormalization approach is powerful compared to purely data-driven symbolic regression, providing an intuitive understanding of data with extrapolative ability.